Two-Factor Authentication: A Short Explanation:
2FA is used to verify your identity with two authentication methods, involving a knowledge factor and another one (possession or inherence). It’s far more secure than SFA, which uses only the knowledge factor (password/passcode) to verify your identity.
Two-factor authentication is implemented as an additional security measure to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Currently, it’s among the most secure authentication options along with the Three-Factor Authentication often used by large organizations and companies.
Two-factor authentication is a process of verifying your identity with two authentication methods as an additional security measure. Usually, it’s required to log in to a specific website, application, or even a device like a smartphone or computer.
As a security measure, it’s pretty important. It prevents unauthorized access and makes it much more difficult for hackers to access your sensitive data, especially in the case of brute-force attacks. In this guide, we’ll explain in detail what is two-factor authentication and see how it works.
What Is Two-Factor Authentication?
Two-factor authentication is also called 2FA, dual-factor, or two-step authentication. This is a crucial security method, which uses two authentication factors to verify your identity. Basically, it’s a type of multi-factor authentication method for protecting your credentials and sensitive data.
But how does it differ from SFA (Single-Factor Authentication)? Well, SFA requires only one factor for verification, which can be a passcode or password. Here, the first factor is a password but the second one can be a biometric factor, security token, a fingerprint, or something else.
This makes it more difficult for hackers and other malicious entities to access your sensitive data. Even if the hacker steals your password, he would need another verification method to access your account. Therefore, he wouldn’t be able to pass the verification process.
How Two-Factor Authentication Works?
We’ve all used 2FA at one point and for some scenarios, it’s necessary. For instance, for Google sign-ups, 2FA is almost always required. If you’re signing in from a new device, Google will require you not only to provide your email and password but also to verify your identity with another factor.
So, how does Two-Factor Authentication work? The first step is your sign in to the website, application, or device. Here, you’re providing your username and password, after which, you’re recognized by the server. Sometimes, the password isn’t required, in which case, the website can provide you with a unique security key.
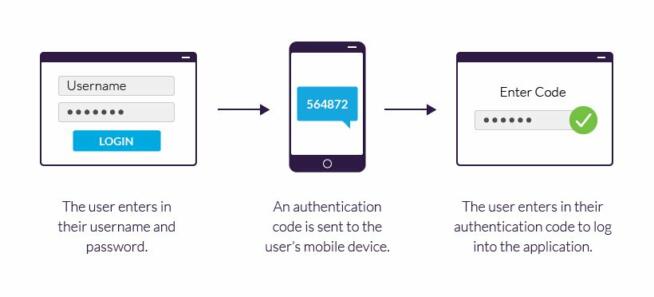
Courtesy of Imperva
This key is processed by the authenticator tool and the key is validated by the server of the website or app that you’re using. Using your email and password is part of SFA but since 2FA requires TWO authentications, the user will be prompted to verify his/her identity as an additional step.
As explained, another bit of required info can be a security token, biometrics, or anything else unique to that user that only he/she possesses. In many cases, it’s a one-time code generated and sent to the user’s email/phone after providing his/her email and password.
When the one-time code or any other authentication factor is used, the user can access the website, device, or application. Two-factor authentication is, as you see, nothing time-consuming and it’s a minor step to securing your account, which is why our team of experts recommends using it whenever viable.
Why Is 2FA Better Than SFA?
SFA and 2FA are vastly different, even though they might seem the same at first. SFA relies on the so-called knowledge authentication. This involves the use of passwords, shared secrets, usernames, emails, and so on. These can be relatively easily obtained by hackers through, let’s say, phishing techniques.
This means you have to be extra careful, think about the passwords you create, and pay attention to the websites you visit. Even then, you’re not 100% safe because hackers use brute-force attacks and other techniques to steal passwords and access sensitive or confidential information.
This is where 2FA comes in, adding another layer of authentication. Apart from the knowledge factor, which we now explained, 2FA can include:
- Possession Factor
- Inherence Factor
A possession factor, logically, is something you possess – a device, for example. That’s how Google functions when it sends you a one-time code to the mobile device associated with you. However, it can also be a security token that you can plug into the USB port on your computer.
An inherence factor is your “personality”, so to speak. It’s facial recognition, voice authentication, fingerprint scan, and so on. This factor is usually implemented for access to physical devices, such as computers, smartphones, servers, and so on.
Is Two-Factor Authentication Really Secure?
While Two-Factor Authentication seems like an idiot-proof method, it’s not. 2FA isn’t impenetrable but its security is superior to SFA. If someone gets a hold of your password and email, your account or device can’t be breached because of possession/inherence factors.
But what if one of these factors is obtained through phishing or malware? Well, that’s where 2FA won’t help you. Authentication factors can be acquired by hackers too, which can still compromise your privacy. Text messages often used for 2FA can also be intercepted by hackers – keep that in mind.
In this case, a hacker can steal the authentication factor and access the account. Physical tokens often used for 2FA are as secure as their issuer’s security is strong. If the issuer gets compromised, chances are that physical tokens will also be compromised as a result.
Despite these risks, 2FA is far more secure than SFA methods for obvious reasons. Of course, Three-Factor Authentication is there too, which includes an additional authentication element – usually all of the three aforementioned factors, including geolocation, device type, and so on.
However, these are mostly used only by large companies and organizations that work with sensitive data.
Summary
In summary, Two-Factor Authentication is almost a surefire way of securing your account and preventing unauthorized access. Being far more secure than Single-Factor Authentication and inexpensive to implement, you’ll find this feature easy to enable for your accounts to keep hackers and snoopers at bay.
We earn commissions using affiliate links.





