OpenVPN Explained Quickly:
OpenVPN is a VPN protocol that establishes a secure tunnel between the VPN client and the server. It uses authentication, with cutting-edge encryption to route data packets through a secure tunnel and ensure they can’t be traced by ISPs and other third parties.
In 2025, it’s one of the top-rated open-source VPN protocols for safety and security. However, OpenVPN suffers from slightly slower speeds, longer connection times, and resource-intensiveness that will affect older hardware the most.
OpenVPN is among the most prevalent tunneling protocols in the VPN industry. As with every protocol, OpenVPN creates a secure tunnel between the VPN client and the server. In this article, we’ll explain what is OpenVPN, see how it works, and discuss its UDP and TCP protocols.
What Is OpenVPN?
OpenVPN stands for Open Virtual Private Network. It’s an open-source protocol used to establish a VPN connection and create a tunnel between networks. To avoid confusion, OpenVPN might also refer to software, which uses the OpenVPN protocol.
Today, we’re discussing the protocol, which is subsequently used by almost all popular VPNs. Some of them include ExpressVPN, CyberGhost, NordVPN, PureVPN and at least hundreds more.
How Does OpenVPN Work?
Okay, so as explained briefly, OpenVPN sets up a secure tunnel between the VPN client and the server. However, in the first stage, it needs to authenticate both. Authentication in OpenVPN works in multiple ways, including public keys, digital certificates, user credentials, and so on.
When this is complete, the tunnel is created and the connection between the VPN client and the server is established. Usually, OpenVPN uses TLS or SSL to create a tunnel but OpenVPN’s flexibility allows for other methods to be used. An important part of how OpenVPN works is encapsulation.
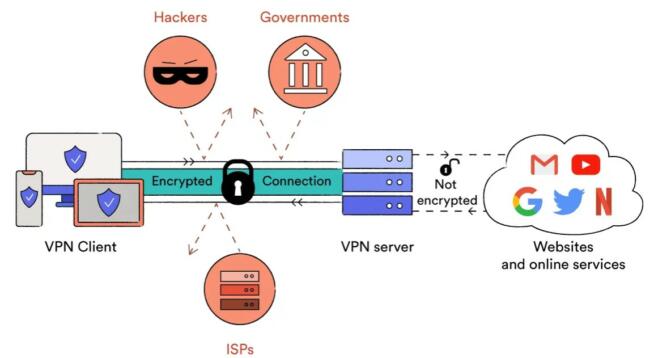
Courtesy of Medium.com
Encapsulation means that OpenVPN encapsulates or wraps data packets with information about the destination, routing, and so forth. In this process, encryption is also applied, which ensures data packets can’t be intercepted and tracked by third parties like ISPs, authorities, employers, and others.
OpenVPN uses AES-256 encryption in most cases, which is the highest encryption standard you can use. Nevertheless, the encrypted data packets travel through the VPN tunnel to the VPN server, they’re decrypted and sent to the final destination.
This decryption shouldn’t scare you – it’s necessary. Before decryption, it passes through the VPN server, which means your original IP address can’t be detected. To anyone inspecting the decrypted data packets, their origin would be the VPN server’s IP address.
How Safe and Secure Is OpenVPN?
Very. It’s an open-source protocol that underwent serious security upgrades. As mentioned, TLS/SSL is used to secure your data, along with PFS (Perfect Forward Secrecy), which assigns unique encryption keys to every connection, preventing data compromises.
On top of that, OpenVPN allows for TCP and UDP protocols to prioritize security or speed – more about that in a second. Its open-source nature means a lot for security. This means cybersecurity experts can inspect the source code and fix bugs and problems within the code.
Alas, this also allows hackers to exploit the code and detect vulnerabilities but then, cybersecurity experts can and will inevitably fix them. OpenVPN works with a plethora of encryption standards and algorithms. This means its security also depends on the encryption the VPN provider chooses to use.
In 99% of the cases, 256-bit encryption is used, which guarantees 360-degree security and no chance of security breach. For this reason, almost all VPN providers use OpenVPN, except Hotspot Shield, UltraVPN, and a few others with proprietary but still OpenVPN-based protocols (Hydra, for example).
OpenVPN UDP vs TCP: Differences Explained
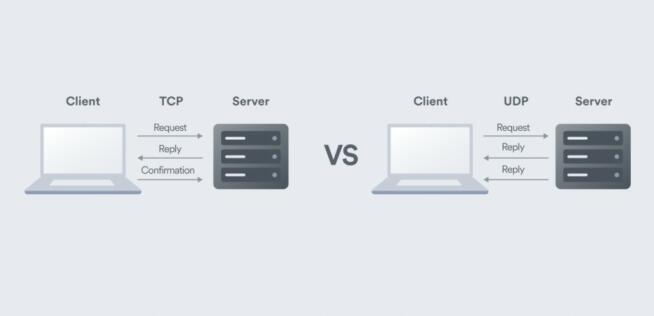
When you use OpenVPN, you’ll usually be able to select from UDP and TCP. UDP stands for User Datagram Protocol. It’s slightly less reliable than TCP but allows for faster speed and sends the packets in a stream. UDP also doesn’t have the error-connection feature from TCP.
That’s why it can send data packets faster but with less reliability. In practice, UDP works very well and is almost always a default OpenVPN option. It’s great for bandwidth-hungry activities like streaming, torrenting, gaming, downloading larger files, and so forth.
Courtesy of Surfshark
TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol and unlike UDP, it’s slower but more reliable thanks to its error-correction feature. Data packets are delivered in a sequence and TCP is more suitable for activities that don’t require fast speed and lots of bandwidth like emailing, browsing, etc.
It’s good to know that TCP is also more reliable for bypassing VPN blocks and restrictions. For instance, NordVPN still uses OpenVPN TCP for its obfuscated servers. They work in China, Iran, and other countries that block VPNs. OpenVPN UDP can’t compete with TCP in this regard.
OpenVPN vs Other Protocols: Is It the Best Option?
While OpenVPN was immensely popular a few years ago, its popularity dwindled a bit recently. IKEv2 is a great protocol too and while it’s faster than OpenVPN, it’s also less resource-intensive. OpenVPN tends to consume more resources and isn’t supported on all systems – iOS, in particular.
Then, we have WireGuard, another open-source protocol that many VPNs adopted. WireGuard is significantly faster and has shorter connection times. In comparison, connecting to a VPN server with OpenVPN takes 5-6 seconds, while WireGuard reduces the time to 1-2 seconds.
NordVPN has NordLynx, an improved version of WireGuard, which is even faster and more secure. ExpressVPN comes with an in-house Lightway protocol, which, in our tests, proved to be faster and more reliable than OpenVPN. So, is OpenVPN the worst protocol out of the bunch? No.
Every VPN protocol has its use and OpenVPN is still used for getting over firewalls, robust encryption, and compatibility with the majority of devices, including routers, Smart TVs, Android phones/tablets, Windows/macOS computers, and many others.
Summary
In summary, OpenVPN remains one of the better VPN protocols in 2025. Its top-of-the-line encryption, superb security, and open-source nature make its implementation possible across a wide range of systems and devices. OpenVPN is, however, not the fastest protocol.
People with older hardware will also find it resource-intensive, producing higher battery drains on older mobile/laptop devices as well. Still, that doesn’t take away from OpenVPN’s tried-and-tested formula, which made the protocol a staple of 99% commercial and corporate VPNs.
We earn commissions using affiliate links.






![Does NordVPN Work With Netflix? [year] – Streaming Tested Does NordVPN Work With Netflix](https://www.privateproxyguide.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Does-NordVPN-Work-With-Netflix-150x150.jpg)









