Due to technological advancements, the internet has become a vital part of our everyday lives. Whether to get in touch with family and friends or keep up with the latest news, everyone is relying on the wonders of Web 3.0 as it’s a great source of information and entertainment as well.
Despite all of its positive contributions, it is inevitable to be aware of the risks that come along with it. People, especially seniors, are more prone to these risks and their adverse effects because they may not be familiar with new tech developments, the use of internet apps, and the smart features available.
In recent years, there has been an increase in online scams that especially targeted seniors and resulted in unfavorable outcomes. Internet scams include fraudulent emails, pop-up ads, and fake websites that are designed to manipulate people and nudge them to share their personal information or money.
1. Rise in Internet Scams against Seniors
Seniors lose billions of dollars each year to internet scams. In the US, seniors who have been scammed reported losses of $1.7 billion in 2021. Moreover, there has been a significant rise in the number of cybercrime complaints filed by seniors in the past. In 2021, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) received more than double the number of complaints from seniors than they did in 2020.
It shows an exponential increase in the number of cybercrime victims within a short period. It is an ethical concern that is leading to devastating outcomes in an online community. As a result of online scams and lack of credibility, many seniors are becoming socially polarized and heading towards social isolation.
2. Why are seniors Prime Targets for Scammers?
Here are some of the key reasons why seniors are prime targets for scammers.
- They are more likely to have significant savings.
- They easily trust strangers and are less likely to suspect that someone is trying to scam them.
- They may be less familiar with how to spot a scam or protect themselves online due to a lack of exposure to technology.
- They are less tech-savvy and lack internet skills.
- They often live alone, which can make them feel isolated and more vulnerable to scams.
- They are less capable of keeping up with the emerging digital world and may not be aware of the latest trends.
This article is aimed to provide a better understanding of various types of internet scams that affect seniors, how to spot such scams, and what to do if you or someone you know becomes a victim of them.
3. Types of Internet Scams
Imagine you are a senior citizen and you receive an unsolicited email from someone claiming to be your bank. The email looks legitimate, with the same logo and branding as your bank’s website. It asks you to click on a link to update your personal information, such as your address, phone number, and social security number. Once you input your information, the scammer now has access to your bank account and can steal your money. Likewise, there are many other types of online scams that can cause serious damage to seniors. The most common online threats include:
3.1 Phishing Scams

These are fraudulent emails that seem to be from a legitimate source, such as a bank or government organization. These emails typically contain a sense of urgency and ask the recipient to click on a link or download an attachment. If people fall for the scam, they will be taken to a fake website that looks real and may be asked to enter personal information, such as their social security number or credit card details. This information can then be used to commit identity theft.
3.2 Pop-up Ads

These are advertisements that appear on websites or in emails. They often contain false claims or promises, such as “You’ve won a prize!” or “Click here to claim your discount.” If you click on the ad, you may be taken to a fake website or asked to enter personal information. In some cases, they may ask you to download malware onto your computer and you might be doing so without realizing it. It can give scammers access to your personal information and even take control of your computer.
3.3 Fake Websites

Some websites are designed to look like legitimate websites, such as websites of government or financial institutions. However, the goal of these websites is to trick senior people and make them enter their personal information or perform any payment transaction. Once the scammers have this information, they can commit identity theft or fraud. The best way to spot a fake website is to check for spelling mistakes, as well as the URL. If it’s a legitimate website, it should start with “https” and there should be a green padlock icon next to the URL.
3.4 Malware Attacks

Malware software is designed to cause damage or disable computers. It can be installed on your computer without your knowledge if you click on a malicious link or download a fake email attachment. Once it is installed, it can collect your personal information or make your computer slow or unusable. Malware attacks can also give the scammers full access to your computer, which they can use to commit fraud or even hold your computer for ransom.
3.5 Ransomware Attacks

This is a type of malware attack where the attacker will encrypt your files and demand a ransom payment to decrypt them. They may also threaten to delete your files or release sensitive information if you don’t pay the ransom. This can be a particularly frightening experience for seniors, who may not have the technical knowledge to deal with such attacks. For ransomware attacks, scammers usually ask to pay the ransom in Bitcoin, as it is very difficult to trace the transactions that are made on the blockchain.
3.6 Social Engineering

Social engineering uses emotionally appealing tactics and scammers often pose as a customer service representative or someone else who needs your information to “verify” your identity. They may even say they are from government entities. They may also do this by pretending to be from a legitimate organization, such as the IRS or your bank. Once they have your information, they can use it for illegal activities.
3.7 Online Auction Scams

With this type of scam, seniors may be tricked into bidding on an item that doesn’t exist or paying for an item that they never receive. The scammer may also set up a fake website that looks like a legitimate online auction site. It’s important to remember that you should only bid on items at sites that you trust. The best way to avoid this type of scam is to do your research before bidding on anything.
3.8 Romance Scams

Romance scammers often create a misleading online profile on a dating website or social media site. They may even send you photos that do not belong to them. They try to build and maintain relationships with seniors and gain their trust. Once they have gained trust, they ask for money or sensitive information. They may even say they need the money for an emergency. This type of scam can be very emotionally devastating, so it’s important to be aware of the signs.
3.9 Investment Scams

In investment scams, you may be promised high returns on investments that don’t exist in reality. The scammer may ask you to wire money or send a payment check. They may also pressurize you to make a quick decision or threaten you by posing that will miss out on this “once in a lifetime” opportunity otherwise. Be very careful before investing any money in anything that you don’t know.
3.10 Sweepstakes and Lottery Scams
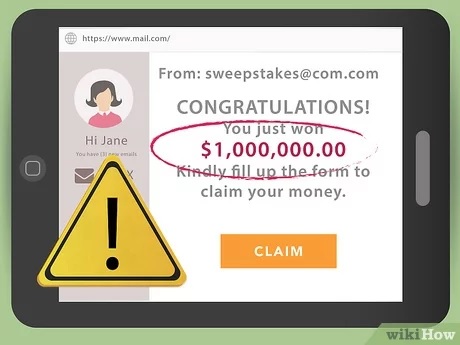
You may receive a call or email encouraging them that you’ve won a prize in a contest or lottery that you didn’t even enter. You will most likely be asked to pay taxes or fees to get rewards. These scammers will often ask for your bank account information so they can “deposit” the money into your account. They may also send you a fake check in the mail.
3.11 Identity Theft

Identity theft is when someone uses your personal information, such as your social security number or credit card number, without your permission. They may do this by stealing your wallet or purse, going through your trash, or hacking your computer. They can also collect your credit card information from restaurants or stores where you have used your card. Once they have your information, they can use it to make purchases, open new credit cards, or even take out loans in your name and rack up debt. That is why it is highly important to use credit cards carefully whether you are using them for online shopping or at physical stores.
3.12 Internet Fraud

This is a catch-all term that refers to any type of fraudulent activity that takes place online. It includes anything from phishing scams and fake websites to investment scams and identity theft. The best way to protect yourself from internet fraud is to be aware of the different types of scams that exist and to take precautions when sharing your personal information or financial information online.
4. How to spot Internet Scams
There are a few different things that you can look for to spot an internet scam targeting seniors. Here are some of the most common signs:
4.1 The offer is too good to be true
If you see an offer that seems too good to be true, it can probably be a scam. For example, if you’re offered a free vacation or a chance to win a prize, it’s likely a scam. For such offers, it is always important to ask for more details and to do your research instead of responding immediately.
4.2 You’re asked to pay upfront
Legitimate businesses will not ask you to pay for something before you receive it. If you’re asked to pay for something with a wire transfer or prepaid debit card, it’s probably a scam. That is why, if someone asks you to pay an upfront fee for anything, you should be very wary.
4.3 You’re asked for personal information
If you’re asked for personal information, such as your social security number or credit card number, be very careful. Only give out this information if you’re sure that you’re dealing with a legitimate company. It is also important to remember that you should never give out your password or credit card PIN to anyone as not even your bank will ask for this information.
4.4 The website looks fake and unprofessional
If the website looks fake or has misspellings, it’s likely a scam. You can also do a quick search online to see if other people have reported the website as a scam. It is also important to remember that even if the website looks legitimate, that doesn’t mean it is. That is why, if you’re ever unsure, it is always best to err on the side of caution.
4.5 You feel pressured to act immediately
Scammers will often try to pressure you into making a decision right away. They may say that the offer is only available for a limited time or that there are only a few spots left. If you feel like you’re being pressured to act immediately, it’s probably a scam.
4.6 The person is pushy or aggressive
If the person you’re dealing with is pushy or aggressive, it’s likely a scam. Scammers will often try to pressure you into deciding before you have time to think about it. While aggressiveness could be another sign that you’re dealing with a scammer. That is why, it is important to take your time when you are talking to someone online, even if they are pressuring you.
5. How Seniors Can Avoid Internet Scams?
Here are a few tips that seniors can follow to prevent internet scams.
5.1 Be skeptical of unsolicited offers
If you’re contacted out of the blue with an offer, be skeptical. Don’t give out personal information or money unless you’re sure that you’re dealing with a legitimate company.
5.2 Don’t pay upfront for something
As mentioned before, legitimate businesses will not ask you to pay for something before you receive it. If you’re asked to pay upfront, it’s most likely a scam. Do not give out your credit card information or wire money to someone you don’t know.
5.3 Do your research
Before doing business with someone, take enough time to do proper research. Check out the company’s website and see if other people have reported it as a scam. In case of an encounter, report such activity, person, or company. In addition to it, share your experience with other seniors and share useful articles that include similar case studies about how individuals have been scammed online.
5.4 Use caution when giving out personal information
Be very careful about whom you give your personal information. Only share your information if you’re sure that you’re dealing with a trustworthy person or a legitimate company. Configure your privacy settings on online applications and social media.
5.5 Keep your computer secure
Make sure that your computer has an active antivirus installed on it and it should be up-to-date. This will help you to protect your device from viruses and other malware attacks. Save copies of your backup data on other devices and any secured cloud as well.
6. Important Guidelines if you become a Victim of Internet Scams
If you think that you’ve been the victim of any online scam, here are a few things that you can do.
6.1 Contact your bank or Credit Card Company
If you’ve given out your financial information to any scammer, contact your bank or Credit Card Company right away. They may be able to help you by canceling fraudulent transactions. You should also change your passwords and PINs and ask your bank to block or deactivate your cards.
6.2 File a report with the FTC
If you’ve been scammed, file a report with the Federal Trade Commission. It will help to prosecute scammers and stop them from deceiving other people.
6.3 File a report with your local police department
In case of being a victim of any fraudulent activity online, file a report with your local police department as well. They may be able to help you get your money back.
6.4 Contact the Better Business Bureau
If you’re dealing with a company that you’re not familiar with or have doubts about, contact the Better Business Bureau. They can provide you with a piece of necessary information if the company is legal or if there have been any complaints filed against the company.
6.5 Spread the word
If you’ve been scammed, warn your friends and family members so they don’t become victims of the same scam. You can also report the scam to websites like Scamalytics and ScamWatch. You should also spread your word by leaving a review on the company’s website or social media page.
7. Final Thoughts
Though the internet is a useful resource for many good reasons, it can cause harm to seniors when it comes to online safety and security. By following the above-mentioned tips, you can protect yourself and other seniors around you from becoming a victim. Be skeptical of unsolicited offers and remember to do your research before responding to any online offers. If you think you’ve been scammed, don’t hesitate to contact your bank, the FTC, or your local police department. And finally, warn your friends and family members to raise online security awareness. You should never feel hesitant to spread your experience as it can save someone else from going through the same thing.
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
8.1 I’m not very tech-savvy. To whom can I talk about internet safety?
You can discuss and take help from your family or friends. Moreover, the FTC has a whole division devoted to helping people with tech-related concerns, including internet safety. You can reach them at 877-382-4357 or visit their website for more information.
8.2 What are the important measures that I can take to stay safe online?
You can take precautionary steps to protect your computer from malware and viruses. Make sure that you have up-to-date anti-virus software installed on your devices. You should also only download programs and apps from trusted sources. Finally, keep your operating system and other applications updated with the latest security patches.
8.3 I’m worried about my personal information being shared online. What can I do to protect it?
Be thoughtful about what you share online. Avoid sharing your birthday, address, or other sensitive information i.e. financial information on social media or other public forums. With the help of privacy settings, control the audience who can see the information you share. Make sure that you have strong passwords for all of your accounts. Avoid using the same password for multiple accounts. You can learn more about protecting your information by visiting the FTC’s website.
8.4 How can I figure out if something is a scam?
If you’re not sure if something is a scam, the best thing to do is to research it before responding. You can read online guides available to prevent online threats and check with the Better Business Bureau. Remember, if something sounds too good to be true, it probably is a scam.
8.5 I think my computer might have been hacked. What should I do?
If you think your computer has been hacked, the first thing you should do is run a security scan to check for malware and viruses. You should also change your passwords for all of your accounts and be cautious about the amount of personal information you share online. If you’re still worried, you can contact the FTC at 877-382-4357 or visit their website for more information.
8.6 What if I want to share any online information with my friends? What could be the safest method?
Before you share anything online, you should always verify if it’s from a trusted source. If you’re unsure about something, the best thing to do is to ask a friend or family member for their opinion. Finally, remember that you can always choose not to share something if you’re not comfortable with it.
We earn commissions using affiliate links.


![How to Reduce Ping in Games [year] – Tips for Faster Gameplay How to Reduce Ping](https://www.privateproxyguide.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/How-to-Reduce-Ping-150x150.jpg)

![Private Internet Access Review: Speed & Security Test [year] private internet access](https://www.privateproxyguide.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/private-internet-access-150x150.jpg)
![Best VPN for UAE & Dubai [year]: Secure Access to the Internet Best VPN for UAE & Dubai 2021](https://www.privateproxyguide.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/Best-VPN-for-UAE-Dubai-150x150.jpg)
![Best VPN for Spectrum ISP [year]: Secure & Fast Internet Access Best VPN for Spectrum ISP 2021](https://www.privateproxyguide.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Best-VPN-for-Spectrum-ISP-150x150.jpg)
![Best VPN for Vodafone [year]: Secure and Fast Internet Access Best VPN for Vodafone](https://www.privateproxyguide.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/Best-VPN-for-Vodafone-150x150.jpg)
![Best VPN for T-Mobile [year]: Secure & Fast Mobile Internet Best VPN for T-Mobile](https://www.privateproxyguide.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/Best-VPN-for-T-Mobile-150x150.jpg)
![Best VPN for SuperHub 3 & 4 [year]: Secure & Fast Internet Best VPN for SuperHub 3 & 4](https://www.privateproxyguide.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Best-VPN-for-SuperHub-3-4-150x150.jpg)
![7 Best VPN for Jio [year]: Secure & Fast Internet Access in India Best VPN for Jio](https://www.privateproxyguide.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Best-VPN-for-Jio-150x150.jpg)
![7 Best VPN for Schools and Colleges [year]: Secure & Private Internet Best VPN for School and College-4](https://www.privateproxyguide.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/Best-VPN-for-School-and-College-4-150x150.jpg)
![Best VPN for Starlink [year]: Secure & Fast Internet Connectivity Best VPN for Starlink-1](https://www.privateproxyguide.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Best-VPN-for-Starlink-1-150x150.jpg)
![7 Best VPN for Satellite Internet [year]: Secure & Fast Connectivity Best VPN for Satellite Internet](https://www.privateproxyguide.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/Best-VPN-for-Satellite-Internet-150x150.jpg)


![MyPrivateProxy Review – Performance, Features & Pricing [year] MyPrivateProxy Review](https://www.privateproxyguide.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/my-private-proxy-150x150.jpg)